In today’s diverse marketplace, packaging has evolved beyond mere product protection to become a critical touchpoint between brands and consumers. Inclusive packaging-designing product containers and wrappings that are accessible and usable by as many people as possible-has emerged as both an ethical imperative and a strategic business decision. With over 61 million adults in the United States living with a disability according to the CDC, the need for packaging that accommodates diverse abilities has never been more apparent.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the principles, benefits, innovations, and future directions of inclusive packaging design, showcasing how brands are reimagining their approach to create more accessible experiences for all consumers.

Understanding Inclusive Packaging
Inclusive packaging refers to designing product packaging that is accessible and usable by the widest possible range of consumers, regardless of age, ability, or circumstance. Rather than following a one-size-fits-all approach optimized primarily for cost-efficiency and visual appeal, inclusive design considers the diverse needs of all potential users-including those with visual, cognitive, and motor impairments.
The concept extends beyond compliance with regulations to create packaging that genuinely enhances the user experience for everyone. From tactile elements and color-contrast optimization to easy-grip structures and larger fonts, inclusive packaging takes many forms that collectively improve usability for all consumers.
Key Principles of Inclusive Packaging Design
Effective inclusive packaging follows several fundamental principles that guide its development:
Equitable Use: Packaging should offer the same ease of use for all users, regardless of their abilities, ensuring equitable access to the product.
Flexibility: Inclusive packaging should be adaptable to a range of preferences, accommodating different abilities and needs.
Simplicity and Intuitiveness: Packaging must be straightforward and easy to understand, catering to users of varying experience levels, knowledge, and skills.
Perceptible Information: Clear communication of key brand or product information is essential, maximizing visibility and ensuring the packaging is easily readable.
Appeal to All: The packaging design should appeal to all potential audience members, considering factors such as color accessibility and contrast, to make it attractive and appealing to a diverse range of consumers.
These principles align with the ISO 1780:2015 standards established by the International Organization for Standardization, which outline guidelines for designing inclusive packaging. These standards emphasize easy access and prompt brands to evaluate factors like the force required to open packages, the potential need for tools, and the user-friendliness of opening mechanisms.
The Business Case for Inclusive Packaging
Implementing inclusive packaging design offers multiple advantages that extend beyond social responsibility to deliver tangible business benefits:
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Thoughtfully designed packaging that is accessible and user-friendly creates a positive experience for all customers, including those with disabilities or specific cultural needs. This fosters brand loyalty and broadens the customer base. When consumers who previously struggled with packaging can now buy and use a product independently, their experience is likely to be positive, fostering feelings of empowerment and trust that translate into a loyal customer base.
Expanded Market Reach
By making products accessible to a wider audience, businesses can tap into diverse markets, leading to increased sales opportunities. Accessible packaging allows individuals with visual impairments, cognitive disabilities, or dexterity challenges to be more independent in their product purchases and use, opening up new market segments.
Competitive Differentiation
Companies that prioritize inclusive packaging design stand out in a crowded marketplace as more consumers seek brands that align with their values. This differentiation helps companies build stronger brand recognition and gain a competitive edge. Accessible packaging is both ethical and strategic, allowing companies to become known for their commitment to social responsibility and form deeper connections with consumers who shop with shared values in mind.
Future-Proofing
As the push for greater inclusivity continues to grow, businesses that take the lead in this area will be better positioned to thrive in the long term. Investing in inclusive packaging is an investment in the future success and sustainability of a brand.

Innovative Examples of Inclusive Packaging
Several brands have pioneered innovative approaches to inclusive packaging, setting new standards for accessibility and usability:
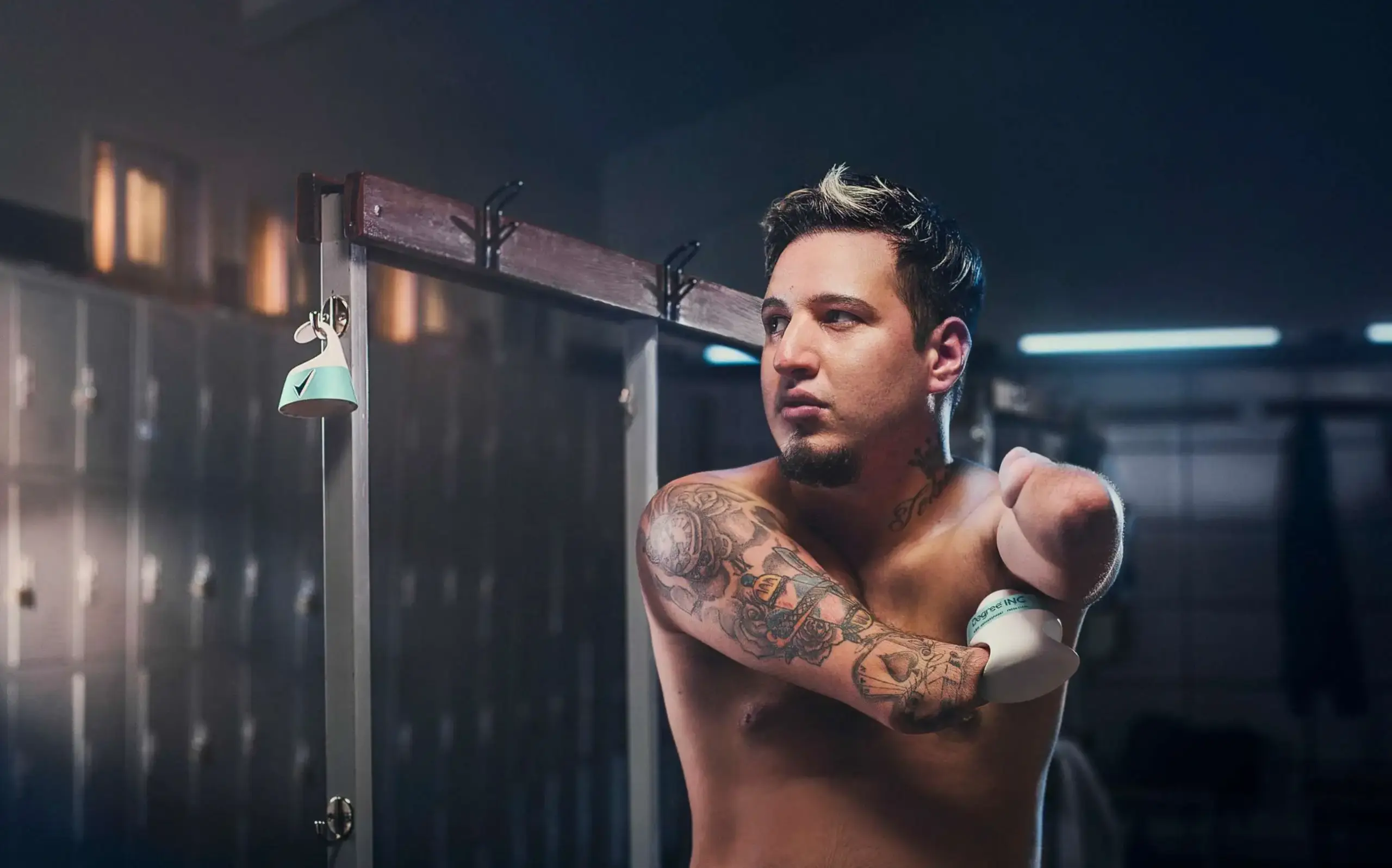
Degree Inclusive
Degree Inclusive is Unilever’s pioneering project in accessible personal care packaging for its Degree brand. Specifically engineered for individuals with visual impairments and upper limb motor disabilities, the deodorant incorporates several groundbreaking features to enhance usability and independence. These include a hook for one-handed application, a magnetic cap that snaps into place with minimal effort, textured grip zones for better control, full braille labeling with detailed instructions, and high-contrast print for users with low vision.
What sets Degree Inclusive apart is its collaborative development process, which included over 200 individuals from the disability community alongside occupational therapists and engineers. Rather than designing for people with disabilities, the product was designed with them—resulting in a user-centric solution that redefines how accessible packaging should look and function. Recognized with major design awards like Cannes Lions, Degree Inclusive not only sets a new industry standard but also highlights how inclusive design can reduce the so-called “disability tax,” restore autonomy, and improve quality of life. Unilever now plans to expand these principles across its product lines and has even shared its design approach openly to drive broader change within the industry.

Herbal Essences Bio-Renew
Herbal Essences Bio-Renew, a product line by Procter & Gamble, became one of the first mainstream hair care brands to integrate tactile differentiation into its packaging to assist visually impaired users. In partnership with the Royal National Institute of Blind People (RNIB) and the Be My Eyes community, the brand introduced a simple yet powerful system: raised stripes for shampoo bottles and circles for conditioner. These tactile markers are strategically placed near the bottom of the bottles where fingers naturally rest, making them intuitive to use without altering the product’s visual design. This innovation was applied consistently across the entire Bio-Renew line, allowing users to reliably distinguish between products without assistance.
By addressing a specific, real-world frustration, the brand set a new industry benchmark and demonstrated how small, thoughtful design changes can yield significant improvements in user experience. The move also exemplifies the “curb-cut effect,” benefiting not just people with disabilities but also sighted users in low-visibility situations. As a result, Herbal Essences has influenced other brands to adopt similar tactile systems, effectively establishing a new standard for inclusive hair care packaging.
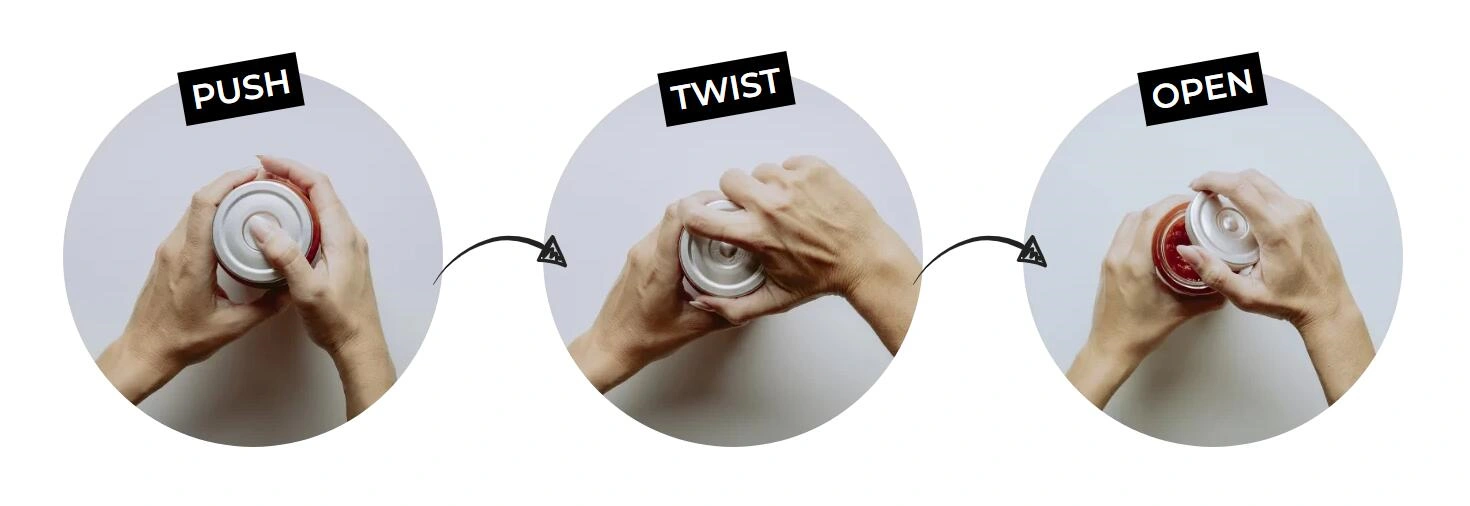
EEASY Lid
The EEASY Lid, developed by Consumer Convenience Technologies (CCT), marks the first major innovation in jar lid design in over 75 years. Targeting one of the most persistent packaging accessibility issues—difficulty opening vacuum-sealed jars—this design introduces a button-activated mechanism that reduces vacuum pressure, thereby lowering the force required to twist off the lid by up to 40%. This improvement is especially impactful for individuals with arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or age-related grip weakness, but its universal design benefits all users, eliminating the need for external tools or unsafe opening methods. Despite its technological advancement, the EEASY Lid preserves traditional jar aesthetics and maintains the same level of food safety and freshness as conventional lids.
From a production standpoint, the lid is available in both aluminum and steel formats, compatible with existing manufacturing equipment and compliant with FDA and European food safety standards. It has already been adopted by several brands and is offered in multiple standard sizes. Consumer response has been overwhelmingly positive, with 88% preferring it over traditional lids—especially those aged 55+ or with hand mobility limitations. The EEASY Lid not only enhances everyday convenience but also exemplifies how inclusive design can become a mainstream feature, solving common problems for a wide demographic while transforming accessibility into a competitive market advantage.
Strategies for Implementing Inclusive Packaging
Designing inclusive packaging involves a holistic approach that considers the diverse needs of all potential users. Here are key strategies to guide the process:
Prioritize Accessibility
Accessibility should be at the forefront of any inclusive packaging strategy, ensuring that packaging is easy to use for people with varying physical, sensory, and cognitive abilities. Tactile elements like Braille labels or embossed symbols can significantly enhance the experience for visually impaired consumers, allowing them to identify and interact with products more independently.
Additionally, using large, high-contrast text ensures that vital information is legible for those with low vision. The design should also account for ease of use; packaging that is difficult to open can be a barrier for individuals with limited dexterity.
Develop Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity in packaging is an important but sometimes overlooked part of inclusive design, especially for global brands. While physical accessibility often gets more focus, cultural accessibility helps ensure that packaging is respectful and relatable for people in different regions. This means understanding how things like colors, symbols, numbers, and text direction can have different meanings in different cultures. For example, white often means purity in the West but mourning in some Asian countries, and the number 4 is avoided in parts of East Asia because it’s linked to death.
To design culturally sensitive packaging, companies often work with local experts and design teams. They may use flexible design systems that keep the brand consistent while allowing for local adaptations. Testing packaging with different cultural groups before launch also helps avoid mistakes. This approach not only prevents expensive errors but also builds trust and stronger connections with customers around the world.
Embrace Universal Design Principles
Universal design is about creating packaging that is intuitive and functional for everyone without the need for adaptation. This strategy emphasizes simplicity and ease of use, ensuring that the packaging works well for the widest range of people.
Minimizing the number of steps required to open the packaging makes the product more accessible to all users, including those with disabilities or limited mobility. Instructions should be clear and straightforward, allowing users to understand how to use the product quickly while maintaining a consistent brand experience.
Test and Iterate
An essential part of designing inclusive packaging is testing designs with real users, especially those from diverse backgrounds or with disabilities. User testing provides valuable insights into how different people interact with packaging, revealing potential issues that might not have been anticipated.
Inclusive design is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. As consumer needs evolve and new technologies emerge, brands must be prepared to iterate and improve their packaging designs. Continuous improvement ensures that packaging remains relevant and effective in meeting the needs of all users.
Ensure Sustainability and Inclusivity
In today’s market, consumers are increasingly conscious of both environmental impact and social responsibility, making it essential for brands to design packaging that addresses both sustainability and inclusivity.
Reducing unnecessary packaging helps maintain functionality and accessibility while minimizing waste without compromising on inclusivity. Brands should consider using recyclable or biodegradable materials that are also easy to open and handle by individuals with disabilities or limited dexterity.

Regional Perspectives on Inclusive Packaging
The adoption and growth of inclusive packaging vary across different regions, reflecting diverse regulatory environments, demographic trends, and market dynamics:
North America
North America dominated the accessible packaging market in 2023 and is expected to continue its stronghold in the coming years. This region’s dominance is attributed to several factors, including stringent regulatory frameworks like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and the ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act), which promote accessibility in various consumer products.
Moreover, the well-established healthcare and pharmaceutical industries in North America are key drivers of market growth. The prevalence of disabilities and chronic conditions, such as arthritis, also contributes to the increasing demand for accessible packaging solutions.
In 2022, arthritis was reported as one of the leading causes of disability in the U.S., affecting a significant portion of the population, particularly older adults. Women were more likely to have arthritis, with a 21.5% prevalence rate compared to 16.1% in men. The impact of arthritis makes tasks such as opening jars, bottles, and other packaging especially challenging, highlighting the need for more user-friendly designs.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is poised to experience the fastest growth in the accessible packaging market during the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to factors such as rapid urbanization, aging populations, and increasing healthcare needs in economies like China, India, and Japan.
In Japan, for instance, the aging rate has steadily increased, with the elderly population over 65 years reaching 36.25 million in September 2024. The number of people aged 80 and older has also grown, reaching 12.9 million, or 10.4% of the total population. This demographic shift is expected to drive demand for accessible packaging solutions tailored to older individuals and those with chronic conditions.
In addition, the region is experiencing a growing demand for functional products such as beverages and supplements, which are expected to further spur market growth. The higher disposable incomes in countries like Japan also play a crucial role in supporting this trend, creating a favorable environment for accessible packaging solutions.
Europe
Europe is expected to maintain steady growth in the accessible packaging market, supported by a combination of regulatory mandates, consumer awareness, and industry innovation. The European Union’s regulatory framework—particularly the European Accessibility Act, which takes full effect across member states by 2025—has been instrumental in pushing manufacturers to adopt inclusive packaging practices. This legal landscape creates a strong foundation for the development and standardization of accessible features such as braille labeling, easy-open mechanisms, and ergonomic design.
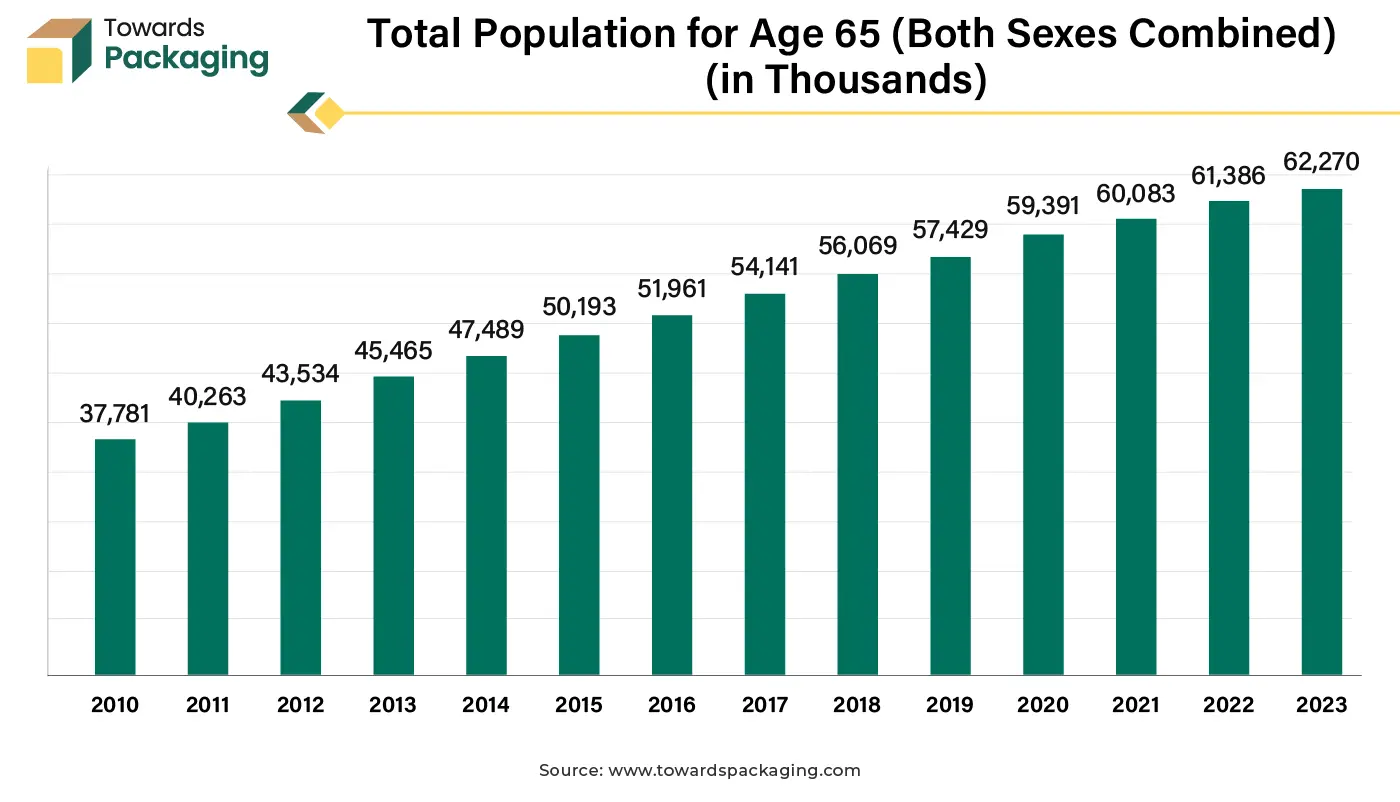
Moreover, Europe’s aging population is a significant market driver. As of 2024, nearly 21% of the EU’s population is aged 65 and over, with countries like Italy and Germany among the oldest in the world. This demographic trend increases the need for packaging that caters to reduced dexterity, visual impairments, and other age-related limitations. Simultaneously, consumer expectations around ethical and inclusive design continue to rise, particularly in Northern and Western Europe, where sustainability and social equity are key purchasing criteria. These factors, combined with the region’s strong healthcare infrastructure and focus on user-centered product development, position Europe as a mature but dynamic market for accessible packaging solutions.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Inclusive Packaging
Technological innovations are further enhancing inclusive packaging, offering new ways to make products more accessible to diverse users:
Smart Packaging
Smart packaging incorporates digital technologies to enhance the functionality and accessibility of packaging. This can include features like QR codes that, when scanned, provide audio messages containing product information such as descriptions, ingredient lists, and usage instructions. This approach, sometimes called “narrative labeling,” enables visually impaired consumers to access comprehensive information that would otherwise be inaccessible to them.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) presents promising opportunities for developing inclusive packaging solutions. AR can provide additional product information or instructions in a user-friendly format, enhancing accessibility for individuals with various disabilities.
Voice-Enabled Instructions
Voice-enabled instructions integrated into packaging can provide audio guidance for product use, making products more accessible to visually impaired users or those with reading difficulties.
Challenges and Opportunities in Inclusive Packaging
While the benefits of inclusive packaging are clear, several challenges and opportunities shape its implementation and evolution:
Challenges
- Balancing Functionality, Cost, and Aesthetics: One of the most significant challenges for manufacturers is balancing functionality, cost, and aesthetic appeal in inclusive packaging designs. Creating packaging that is both accessible and visually appealing while maintaining cost-effectiveness requires careful consideration and innovative approaches.
- Lack of Global Standards: The absence of global standards for what constitutes ‘inclusive packaging’ can lead to inconsistency in adoption and consumer confusion. Without clear guidelines, companies may interpret inclusivity differently, resulting in varying levels of accessibility across products and brands.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: External factors such as geopolitical conflicts and economic downturns can disrupt the supply chain for inclusive packaging materials, leading to shortages and increased costs. These disruptions can hinder the adoption and implementation of inclusive packaging solutions.
Opportunities
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in technology, such as augmented reality and smart packaging, provide opportunities for creating more inclusive packaging solutions. These innovations enable packaging to go beyond traditional functions, offering interactive and intelligent features that enhance user experience, accessibility, and inclusivity.
- Untapped Markets: There is untapped market potential in developing regions where awareness of inclusive packaging is still emerging. As these markets grow and evolve, companies that prioritize inclusivity can gain a competitive advantage and establish themselves as leaders in accessibility.
- Innovation During Economic Downturns: Despite challenges, economic downturns can spur innovation in the inclusive packaging market. Companies may leverage inclusive packaging to differentiate themselves and attract consumers seeking added value, convenience, and accessibility.

The Future of Inclusive Packaging
As we look ahead, several trends and developments are likely to shape the future of inclusive packaging:
Integration of Advanced Technologies
The integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices will further enhance the accessibility and functionality of packaging. These technologies can enable more personalized and adaptive packaging solutions that cater to individual needs and preferences.
Greater Emphasis on Universal Design
The concept of universal design-creating products that are usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design-will gain greater prominence in packaging development. This approach will lead to more inclusive packaging solutions that benefit all consumers, regardless of their abilities.
Increased Collaboration and Standardization
Greater collaboration among industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and advocacy groups will likely lead to more standardized approaches to inclusive packaging. This collaboration can help establish clearer guidelines and best practices for designing and implementing accessible packaging solutions.
Sustainability and Inclusivity Integration
The integration of sustainability and inclusivity will become increasingly important as consumers demand packaging that is both environmentally friendly and accessible. Companies will need to find innovative ways to balance these sometimes competing priorities to create packaging that meets both environmental and accessibility standards.
Conclusion
Inclusive packaging represents a significant shift in how brands approach product design and consumer engagement. By considering the diverse needs and abilities of all potential users, companies can create packaging that is not only more accessible but also more user-friendly for everyone.
The business case for inclusive packaging is compelling, offering benefits such as enhanced customer satisfaction, expanded market reach, competitive differentiation, and future-proofing. As technology continues to advance and consumer expectations evolve, the importance of inclusive packaging will only grow.
Leading brands across various industries have already demonstrated the potential of inclusive packaging through innovative designs and approaches. From tactile indicators and easy-open mechanisms to smart packaging and voice-enabled instructions, these innovations are making products more accessible to diverse users.
While challenges remain, the opportunities for growth and innovation in inclusive packaging are substantial. By embracing the principles of inclusive design and leveraging emerging technologies, companies can create packaging solutions that truly work for everyone, fostering a more inclusive and accessible marketplace.
As we move forward, the integration of inclusivity into packaging design will likely become not just a competitive advantage but a standard practice-reflecting a broader societal shift toward greater accessibility and inclusion for all individuals, regardless of their abilities or circumstances.