Barrier layers are the unsung heroes of cosmetic tube packaging, ensuring that creams, gels, and serums reach consumers with their efficacy, texture, and safety intact. These specialized internal layers act as protective shields, forming a critical barrier between the product and external threats such as oxygen, moisture, light, and microbial contaminants. Without effective barrier technology, active ingredients like antioxidants, vitamins, and botanical extracts can degrade rapidly, leading to diminished performance, shorter shelf life, and compromised user safety.
As the beauty industry evolves—driven by consumer demands for clean beauty, sustainability, and premium experiences—the science and innovation behind barrier layers have become central to both product preservation and environmental stewardship. Brands are increasingly investing in advanced materials and multi-layer technologies that not only safeguard sensitive formulations but also address growing concerns about recyclability and environmental impact. Innovations such as mono-material tubes, bio-based barriers, and recyclable laminates are reshaping the landscape, reflecting a shift toward packaging that balances high performance with eco-conscious design.
This expanded article explores the science, technology, market trends, and real-world case studies that illuminate the critical role of barrier layers in cosmetic tubes, highlighting how these invisible protectors underpin both product quality and the industry’s sustainability journey.

The Science and Purpose of Barrier Layers
Barrier layers are specialized materials or coatings integrated within cosmetic tubes to serve as protective shields for sensitive formulations. Their primary function is to defend the product against a range of external threats that can compromise the efficacy, safety, and sensory qualities of creams, gels, and serums. Here’s how these threats are addressed:
- Oxygen:
Exposure to oxygen is a leading cause of degradation for many cosmetic ingredients. Active compounds like vitamin C and retinol are particularly prone to oxidation, which results in the loss of their intended benefits and can even lead to spoilage or discoloration. Barrier layers—often made from materials such as aluminum foil or EVOH (ethylene vinyl alcohol)—dramatically reduce oxygen transmission into the tube, thereby prolonging shelf life and preserving ingredient potency.
- Moisture:
Moisture ingress can destabilize emulsions, alter the texture of the product, and promote the growth of microbes. This is especially critical for water-based formulations or those with minimal preservatives. High-quality barrier layers act as a moisture lock, maintaining the desired consistency and safety of the formula throughout its lifecycle.
- Light (especially UV):
Many cosmetic actives are sensitive to light, particularly UV rays, which can break down molecules and reduce product efficacy. Aluminum barriers and certain plastics with UV-blocking additives are used to shield contents from harmful light exposure, ensuring that light-sensitive ingredients remain effective until the last use.
- Contaminants:
Once a tube is opened, the risk of contamination from bacteria or airborne particles increases. Airless and pump tubes, often combined with multi-layer barrier technology, limit the entry of contaminants during dispensing, supporting product hygiene and user safety.
Key Barrier Metrics to Consider
When selecting the right barrier layer for your cosmetic tube, it’s important to evaluate specific performance metrics that determine how well your product is protected:
- Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR)
This measures how much oxygen passes through the material over a given time. Lower OTR values mean stronger protection against oxidation—a critical factor for serums, oils, and vitamin-rich formulas that degrade in air.
- Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR)
WVTR tracks the rate at which moisture penetrates the tube wall. A low WVTR helps preserve the consistency and stability of water-based or emulsion-type products, making it essential for creams and lotions.
- Light Transmission
This indicates how much UV and visible light passes through the tube material. A high barrier to light—particularly UV rays—prevents degradation of sensitive ingredients like retinol, vitamin C, and essential oils. Materials like ABL or UV-coated PBL tubes often offer excellent light shielding.

Barrier Materials and Technologies
Barrier technologies are at the core of modern cosmetic tube packaging, ensuring that sensitive formulations are protected from environmental threats while also addressing the growing demand for sustainability and recyclability.
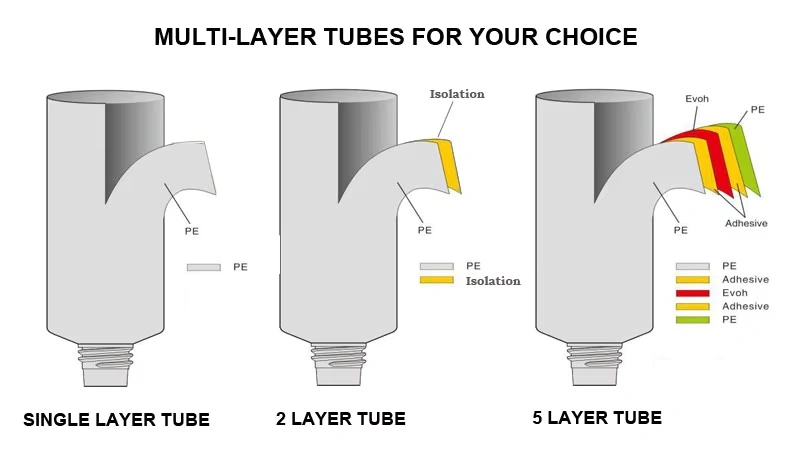
Multi-Layer Barrier Tubes
Most high-performance cosmetic tubes employ multi-layer structures, where each layer serves a distinct function—combining strength, flexibility, and barrier protection.
- Aluminum Barrier Laminate (ABL)
Structure: ABL tubes feature a thin aluminum layer sandwiched between layers of polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP).
Performance: The aluminum core provides exceptional protection against oxygen, moisture, and light, making ABL tubes ideal for highly sensitive, luxury, or pharmaceutical formulations that require maximum preservation of actives and shelf life.
Applications: Aggressive products (liniment creams, antiseptics), essential oils, high-end skincare, and sunscreens.
Drawbacks: While aluminum enhances barrier performance, it introduces recyclability challenges due to material incompatibility and metallization, which often prevent plastic tubes from meeting high recyclability targets (such as the 70% benchmark in the EU).
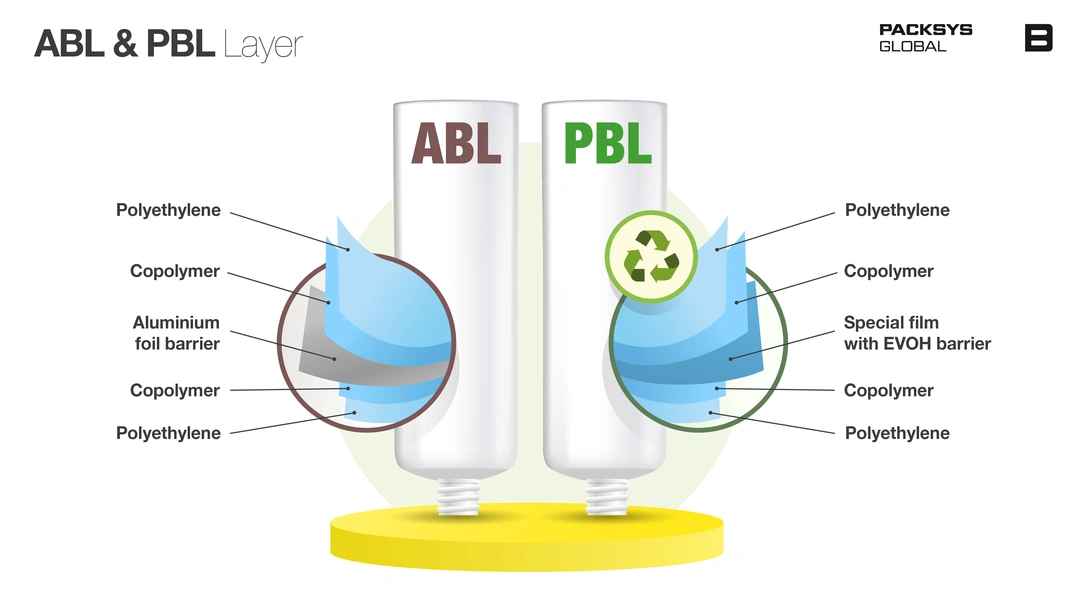
- Plastic Barrier Laminate (PBL)
Structure: PBL tubes are composed entirely of plastic layers—commonly PE, PET, and EVOH (ethylene vinyl alcohol)—without aluminum.
Performance: PBL tubes offer strong barrier properties (especially against oxygen and moisture) and are lighter and more recyclable than ABL tubes. The inclusion of EVOH as a barrier layer is particularly effective in blocking oxygen and preventing oil migration.
Applications: Widely used in cosmetics, personal care, pharmaceuticals, and food products, PBL tubes are valued for their clarity, customizable artwork, and ability to maintain their shape after handling.
Advantages: Enhanced clarity, premium surface treatments, and improved recyclability compared to ABL.
- EVOH (Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol)
Role: EVOH is a high-performance gas barrier resin frequently co-extruded between PE or PP layers in both ABL and PBL tubes.
Benefits: EVOH provides excellent oxygen resistance, which is vital for preserving the freshness and efficacy of sensitive ingredients. It is flexible, moldable, and can be recycled when used in small proportions within mono-material systems.
Limitation: EVOH is sensitive to moisture and must be encapsulated by hydrophobic layers to maintain its barrier properties.
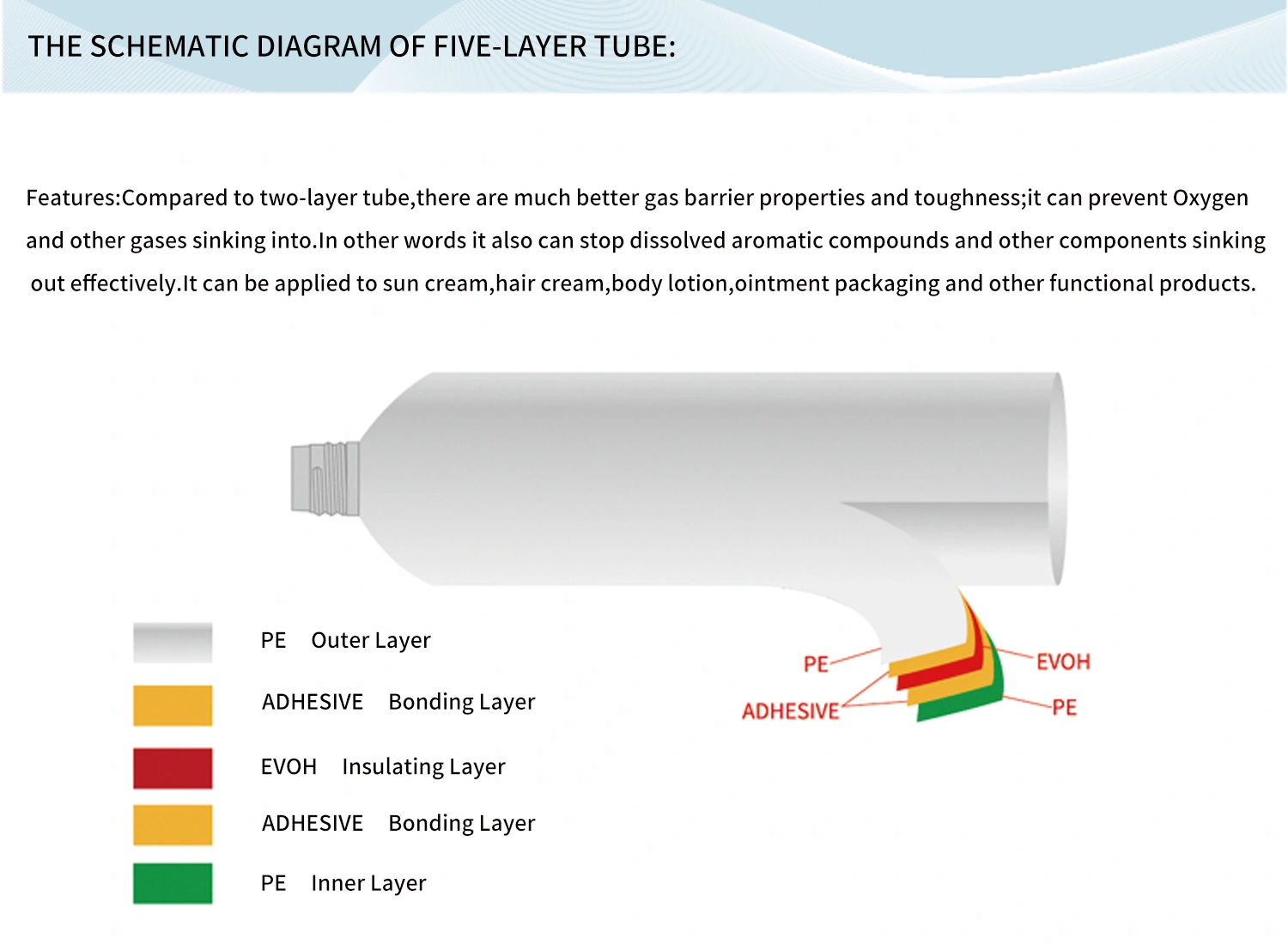
- Multi-Layer Construction
Design: Modern cosmetic tubes can feature up to five or more layers, each serving a specific purpose—outer printability, mechanical strength, barrier protection, and product compatibility.
Benefits: This construction provides superior protection against air, moisture, and light, ensuring stability and longevity for sensitive formulations.
Innovations in Barrier Coatings and Hybrid Materials
As the industry pivots toward sustainability, new coatings and hybrid structures are emerging to balance barrier performance with eco-friendliness.
• Biodegradable and Water-Based Coatings
Overview: Water-based and biodegradable coatings are being developed for paper and cellulose tubes, offering moisture and grease resistance while enabling compostability.
Materials: Innovations include coatings derived from cutin, chitosan-chitin, and proteins, which can provide hydrophobic, antimicrobial, or gas barrier properties.
Industry Example: Solésence Beauty Science and H.B. Fuller are pioneering water-based barrier coatings that improve recyclability and fiber yield in paper-based packaging.
• Hybrid Structures
Approach: Hybrid tubes combine renewable fibers (such as molded pulp) with micro-thin barrier films, maintaining product efficacy while allowing for curbside recycling or industrial composting.
Challenge: These structures must balance high barrier performance with compatibility in existing recycling streams and withstand conventional manufacturing processes.
• Plasma-Based Coatings
Technology: Plasma-enhanced vapor deposition applies ultra-thin, chemically inert nanocoatings to plastics, glass, or metals, significantly improving barrier properties without adding bulk or compromising recyclability.
Benefits: These coatings can be tailored for hydrophilic or hydrophobic properties, corrosion protection, and long-term stability, supporting both sustainability and product preservation.
Mono-Material Solutions
To address recycling challenges, the industry is rapidly adopting mono-material tubes—packaging made from a single type of plastic, typically HDPE or PE, with advanced barrier coatings.
Advantage: Mono-material tubes are fully compatible with mainstream recycling streams, achieving the highest standards for recyclability (e.g., RecyClass certification).
Barrier Performance: Recent advances allow mono-material tubes to match the barrier properties of traditional multi-layer and ABL tubes, even offering airless solutions and compatibility with post-consumer recycled (PCR) and bio-based plastics.
Industry Movement: Major brands are transitioning from multi-material to mono-material packaging to future-proof their products against stricter regulations and consumer expectations for circularity.
Market Trends and Consumer Demands
Demand for High-Barrier Packaging
Today’s consumers expect both efficacy and sustainability. High-barrier tubes are essential for:
Preserving advanced formulations: Modern skincare and cosmetics often contain actives that degrade quickly without robust protection.
Meeting luxury and mass-market needs: Both high-end and mainstream brands seek visually appealing, durable, and sustainable tubes.
E-commerce: Increased online shopping requires tamper-evident, tough packaging that can withstand shipping and handling.
Sustainability and Recycling Challenges
Multi-Layer Recycling Issues: Traditional multi-layer tubes (especially those with aluminum or mixed plastics) are difficult to recycle. Most recycling facilities are equipped to handle single-material plastics, so multi-layer tubes often end up in landfills.
Industry Response: Initiatives like the Tube Recycling Project have led to major advancements, with a growing number of toothpaste and cosmetic tubes now compatible with mainstream recycling streams.
Bio-Based and Compostable Barriers: Brands are experimenting with sugarcane-based PE, PLA, and biodegradable coatings that offer protection without sacrificing compostability or recyclability.
Regulatory and Transparency Pressures
Regulatory Compliance: Tube materials must meet FDA and other regulatory standards for safety and compatibility.
Transparency: Consumers expect brands to disclose material origins, biodegradability, and recyclability. Greenwashing is increasingly scrutinized, making transparency a competitive advantage.
Technological Innovations
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Coextrusion: Allows for precise layering of barrier materials (e.g., EVOH, PA) within a single tube wall, optimizing protection while minimizing material use.
In-Mold Barrier (IMB) Technology: Integrates barrier layers directly into HDPE molding, resulting in fully recyclable mono-layer packaging with excellent resistance to permeation.
Digital Printing and Prototyping: Enables rapid design changes and customization without compromising the barrier properties of the tube.
Smart and Functional Packaging
Airless Tubes: Incorporate barrier layers and pump mechanisms to prevent air and contaminants from entering, ideal for preservative-free or sensitive formulations.
Tamper-Evident Seals: Essential for e-commerce and regulatory compliance, these features are often integrated into high-barrier tubes.
Connected Packaging: QR codes, NFC chips, and smart labels can be embedded without affecting barrier integrity, providing authentication and consumer engagement.

Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Barrier Layer Innovation
Transforming Toothpaste Tube Recycling in the UK
- Background
Toothpaste tubes have historically posed a significant challenge for recycling efforts due to their complex multi-layer construction. Traditionally, these tubes combined layers of plastic and aluminum to provide the necessary barrier protection for sensitive formulations. However, this mixed-material approach rendered the tubes non-recyclable in most municipal systems, leading to their disposal in landfills and contributing to mounting plastic waste. The inability to recycle these tubes represented a missed opportunity for circularity and sustainability in everyday consumer products.
- Solution
Recognizing the environmental impact and regulatory pressures, leading oral healthcare brands—including Haleon, Colgate-Palmolive, Unilever, and P&G—joined forces with the UK sustainability organization WRAP to address the issue. Through industry-wide collaboration, they pioneered the transition to mono-material toothpaste tubes made entirely from polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP). These new tubes were engineered to deliver the same protective barrier properties as their predecessors but without the aluminum layer. As a result, the redesigned tubes became fully compatible with the UK’s kerbside recycling infrastructure, meeting national standards for household plastic recycling.
- Impact
Enabled Circularity: The shift to mono-material tubes allowed for true circularity in plastics, ensuring that used tubes could be collected, processed, and remanufactured into new products, thus reducing reliance on virgin materials and minimizing landfill waste.
Improved Recovery Rates: Properly emptied mono-material tubes achieved a 60% recovery rate in recycling streams, a significant improvement over the mere 16.7% recovery rate for partially filled tubes. This highlights the importance of consumer education in maximizing recycling efficiency.
Legislative Readiness: By adopting recyclable tubes, brands future-proofed their packaging against evolving environmental regulations, reducing potential compliance costs and risks associated with non-recyclable materials.
Cost Savings: The move to recyclable materials helped brands lower long-term costs tied to waste management and non-compliance, while also enhancing their sustainability credentials.
Industry Influence: This collaborative success set a precedent for other sectors—such as cosmetics and pharmaceuticals—demonstrating that industry-wide action and innovation can overcome recyclability barriers and accelerate the adoption of circular packaging solutions.
- Key Takeaway
This case study underscores the transformative power of industry collaboration and technological innovation. By transitioning from complex multi-layer constructions to mono-material barrier tubes, the oral care sector dramatically improved recyclability and sustainability. The benefits extend beyond environmental gains, offering regulatory, economic, and reputational advantages for brands. This model of collaboration and material innovation is now influencing broader packaging trends, including those in cosmetic and pharmaceutical packaging, and serves as a blueprint for achieving circularity in other challenging product categories.
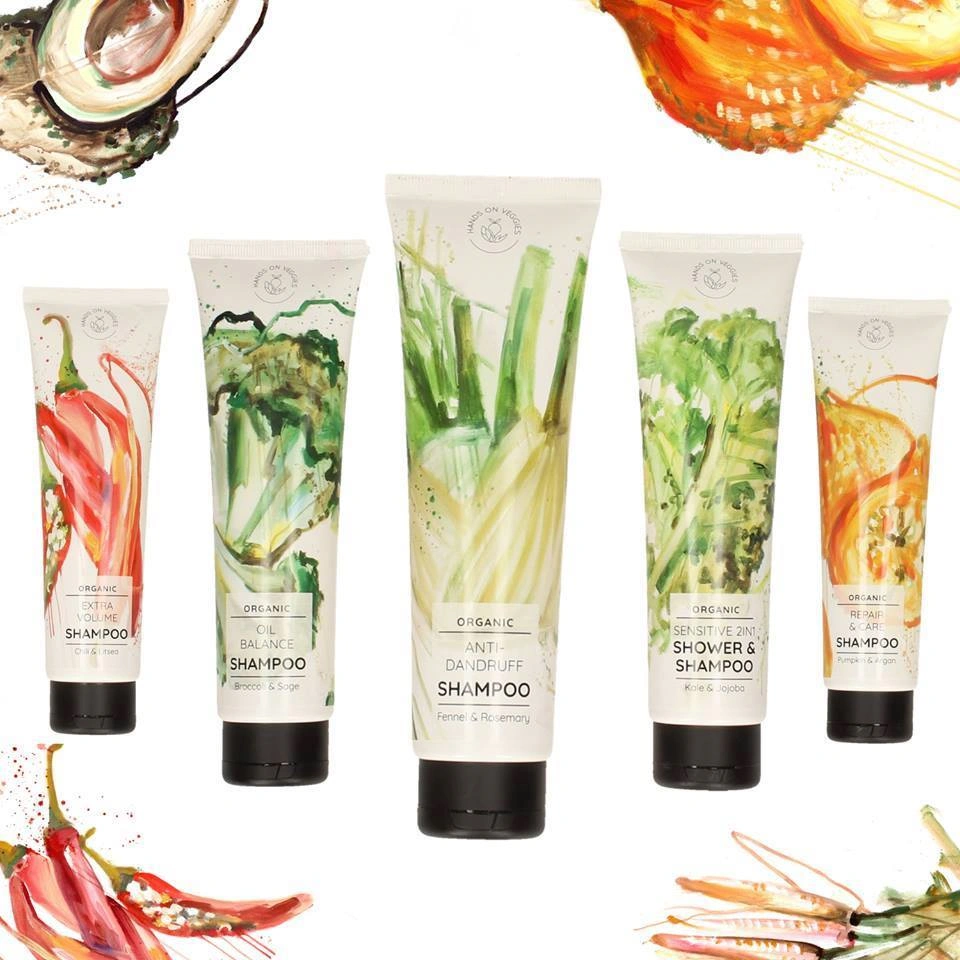

Hands on Veggies: Bio-Based Polyethylene Tubes for Natural Cosmetics
• Background
Austrian organic cosmetics brand Hands on Veggies was founded on a commitment to plant-based, sustainable products. The company sought packaging that would align with its eco-conscious ethos, aiming for a solution that was both environmentally friendly and capable of preserving the quality of its natural formulations.
• Solution
To achieve this, Hands on Veggies partnered with FKuR, a leader in bioplastic solutions, and adopted tubes made from Braskem’s “I’m green™” bio-based polyethylene (Bio-PE). This material is derived from renewable sugarcane, offering a significantly reduced carbon footprint compared to conventional fossil-based plastics. The Bio-PE tubes exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including robust barrier effects against water vapor, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and shelf life of organic cosmetic products.
Importantly, these tubes are fully recyclable within the standard PE waste stream, supporting a circular economy and making it easier for consumers to dispose of the packaging responsibly. The material’s compatibility with existing manufacturing equipment meant that Hands on Veggies could implement this sustainable solution without any changes to their processing lines, demonstrating the practicality of bio-based plastics as a direct replacement for traditional polymers.
Additionally, the Bio-PE tubes allow for high-quality, customizable printing. This enabled Hands on Veggies to maintain its distinctive artistic branding and communicate its natural identity directly on the packaging, further strengthening its market position as a sustainable and creative brand.
• Impact
Holistic Sustainability: The switch to bio-based tubes provided a comprehensive eco-friendly solution, addressing both the product’s ingredients and its packaging.
Barrier Performance: The tubes maintained essential barrier properties, ensuring product preservation and extending shelf life, which is particularly important for natural and preservative-free cosmetics.
Brand Identity: The ability to print high-quality, custom designs on the tubes supported Hands on Veggies’ brand messaging and visual appeal.
Operational Efficiency: The drop-in compatibility of Bio-PE meant no additional investment in new machinery or processes was required, facilitating a smooth transition to greener packaging.
• Key Takeaway
Hands on Veggies’ adoption of bio-based barrier tubes demonstrates that it is possible to achieve both sustainability and high performance in cosmetic packaging. Bio-PE tubes offer a viable, scalable, and effective solution for brands aiming to meet consumer expectations for eco-friendly beauty products—without sacrificing product protection or visual impact. This case sets a benchmark for other cosmetic companies seeking to align their packaging strategy with environmental stewardship and brand authenticity.

L’Oréal’s Sugarcane-Based Tubes—Sustainability Meets Performance
• Background
L’Oréal, one of the world’s leading beauty conglomerates, has made significant strides in sustainable packaging as part of its broader environmental commitments. Recognizing the environmental impact of conventional fossil-based plastics, L’Oréal sought to develop packaging solutions that reduce carbon footprint while maintaining the high standards required for cosmetic product protection.
• Solution
L’Oréal introduced bio-based tubes made from renewable sugarcane-derived polyethylene for several of its flagship brands, including Garnier and La Roche-Posay. These sugarcane-based tubes offer a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. The process involves converting sugarcane ethanol into polyethylene, resulting in a material that is chemically identical to conventional PE but with a significantly lower environmental impact.
Crucially, these tubes are engineered to maintain the essential barrier properties needed to protect sensitive cosmetic formulations from oxygen, moisture, and light. This ensures that the switch to renewable materials does not compromise product efficacy or shelf life—a key consideration for brands with global reach and diverse product portfolios.
• Impact
Sustainability: The use of sugarcane-based polyethylene reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions, supporting L’Oréal’s sustainability targets.
Performance: The tubes retain the necessary barrier qualities to safeguard product integrity, demonstrating that eco-friendly materials can meet the rigorous demands of the cosmetics industry.
Recyclability: L’Oréal’s sugarcane-based tubes are fully recyclable within existing PE waste streams, facilitating consumer participation in circular economy practices.
Brand Leadership: By rolling out these tubes across major brands, L’Oréal sets a benchmark for sustainable innovation in the beauty sector and encourages other companies to follow suit.
• Key Takeaway
L’Oréal’s adoption of sugarcane-based tubes exemplifies how large-scale brands can successfully integrate renewable materials into their packaging without sacrificing performance. This initiative demonstrates that sustainability and product protection can go hand in hand, and it aligns with growing consumer expectations for eco-conscious beauty products. The move also reinforces L’Oréal’s position as an industry leader in sustainable packaging innovation.
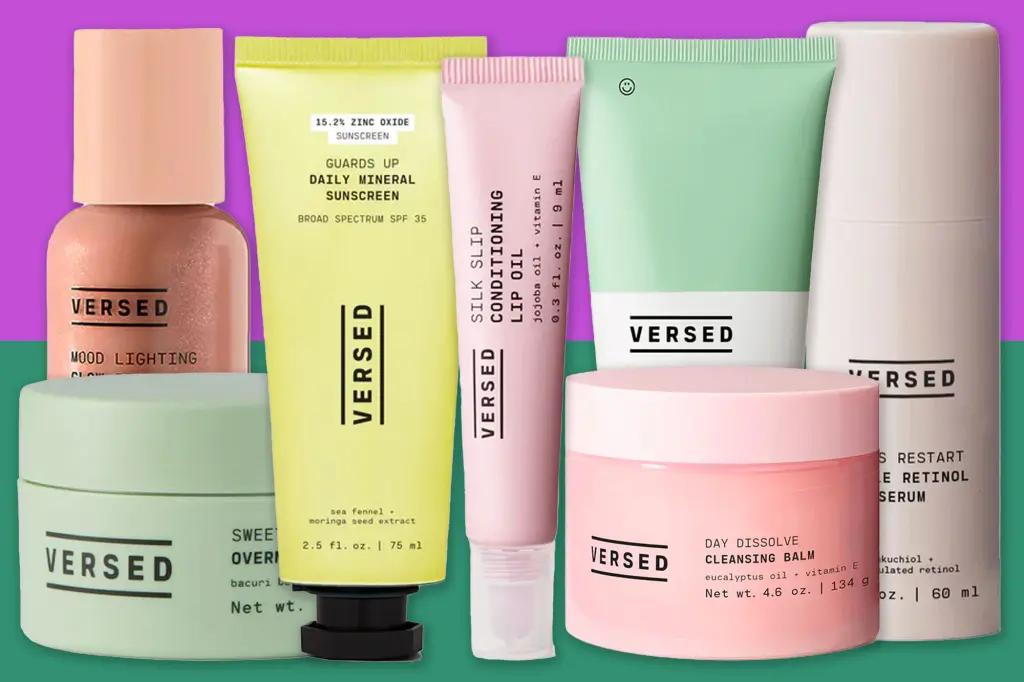

Versed—Aluminum and PCR Tubes for Clean Skincare
• Background
Versed, a leading clean skincare brand, is committed to transparency and sustainability in both its formulas and packaging. Recognizing the importance of packaging in preserving product integrity and minimizing environmental impact, Versed strategically employs both aluminum and PCR (post-consumer recycled) plastic tubes across its product lineup.
• Solution
Aluminum Tubes:
Aluminum is renowned for its superior barrier properties, offering exceptional protection against light, air, and moisture. This makes it an ideal choice for Versed’s natural or preservative-free formulations, as it helps prevent oxidation, microbial growth, and ingredient degradation. Aluminum tubes also offer the advantage of being infinitely recyclable without loss of quality, supporting long-term circularity in packaging.
PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) Tubes:
Versed also utilizes tubes made from PCR plastics, which are sourced from recycled consumer waste. By incorporating PCR materials, Versed reduces its reliance on virgin plastics, lowers its carbon footprint, and supports the development of a circular economy. PCR tubes maintain the necessary mechanical and barrier properties to protect skincare products while aligning with consumer expectations for eco-friendly packaging.
• Impact
Product Protection: Aluminum tubes ensure that light- and air-sensitive ingredients remain stable and effective, extending shelf life and maintaining product safety.
Sustainability: The use of PCR tubes diverts plastic waste from landfills and reduces the demand for new plastic production, supporting resource conservation and environmental stewardship.
Circular Economy: Both aluminum and PCR tubes are recyclable, enabling Versed’s packaging to be reprocessed into new materials and products, thus closing the loop on packaging waste.
Brand Positioning: By transparently communicating its packaging choices, Versed appeals to eco-conscious consumers and reinforces its leadership in clean, sustainable skincare.
• Key Takeaway
Versed’s dual approach—employing both aluminum and PCR tubes—demonstrates that brands can deliver high-performance product protection while advancing sustainability goals. This strategy not only preserves the efficacy and safety of clean skincare formulations but also supports a circular economy, setting a strong example for the beauty industry’s transition toward more responsible packaging solutions.

Sustainability: The Next Frontier
Overcoming Recycling Barriers
Mono-Material Tubes: The industry is moving toward single-material tubes (e.g., all-PE or all-HDPE) with advanced barrier coatings, making them compatible with existing recycling systems.
Chemical Recycling: Emerging technologies can break down multi-layer tubes into raw materials for new packaging, though scalability and cost remain challenges.
Bio-Based Barriers: Water-based, biodegradable coatings and PLA films are being developed to provide necessary protection while allowing for industrial composting.
Life Cycle and Environmental Impact
Material Recovery: Adhesives and coatings in barrier tubes can complicate recycling, often requiring specialized processes.
End-of-Life Solutions: Brands are increasingly transparent about the recyclability and compostability of their packaging, responding to consumer demand for low-impact solutions.
Regional Perspectives
North America
- Recycling Leadership:
The United States has emerged as a leader in making toothpaste and cosmetic tubes compatible with mainstream recycling systems, particularly HDPE bottle recycling streams. Industry-wide initiatives and collaborations with recyclers have enabled most new tubes—especially those made from mono-material HDPE or PE—to be collected, sorted, and reprocessed alongside milk jugs and detergent bottles. This compatibility has set a benchmark for the global industry and significantly improved the circularity of cosmetic and personal care packaging.
- Innovation Hubs:
North America is also a hotspot for rapid adoption of advanced barrier technologies. Both mass-market and prestige brands are embracing:
Airless tubes for preservative-free and sensitive formulations,
EVOH barrier layers for enhanced oxygen protection,
Mono-material tubes that balance recyclability with high barrier performance.
These trends are driven by consumer demand for clean beauty, regulatory pressure, and a strong focus on sustainability and product efficacy.
Europe
- Sustainability Leadership:
European brands and regulators are at the forefront of sustainable packaging innovation. There is a strong push for:
Mono-material tubes that are easy to recycle,
Compostable and bio-based tubes for luxury and natural beauty categories,
Reduction of multi-layer and metallized structures in favor of simpler, more sustainable designs.
- Regulatory Standards:
Europe enforces strict packaging regulations, including adherence to EN 13432 for compostability and other certifications that guarantee recyclability and minimal environmental impact. These standards have accelerated the adoption of innovative barrier materials and eco-friendly solutions, particularly among luxury and organic brands seeking to align with both consumer expectations and legal requirements.
Asia-Pacific
- Market Growth:
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region for barrier tube packaging, fueled by a booming beauty and personal care market and rising demand for advanced skincare. The region’s consumers are increasingly seeking products that offer both efficacy and premium packaging.
- Localization:
Manufacturers in Asia-Pacific are tailoring barrier tube designs to address specific climate challenges, such as high humidity in tropical regions. Enhanced moisture barriers and humidity-resistant materials are commonly used to ensure product stability and shelf life. Additionally, rapid urbanization and digital engagement drive innovation in packaging formats and smart features, catering to tech-savvy and trend-sensitive consumers.

Future Directions and Challenges
Technical and Economic Barriers
Cost: High-performance barrier materials (like EVOH or plasma coatings) can be 20–30% more expensive than standard plastics.
Recycling Infrastructure: While mono-material solutions are promising, global recycling infrastructure must catch up to handle new materials and designs.
Performance vs. Sustainability: Achieving both high barrier performance and full recyclability/compostability remains a key challenge.
Next-Generation Innovations
Plasma-Based and Nanocoatings: Ultra-thin, recyclable coatings offer robust protection without compromising sustainability.
Hybrid Fiber Structures: Combining renewable fibers with micro-barriers for recyclable, compostable tubes.
Active and Intelligent Barriers: Future tubes may incorporate self-healing barriers or active layers that neutralize contaminants or provide real-time freshness indicators.
Conclusion
Barrier layers in cosmetic tubes are more than just invisible shields—they’re the secret ingredient that lets your favorite creams and serums arrive fresh, safe, and effective every time you open the cap. As the beauty world races toward cleaner, greener, and more luxurious experiences, these unsung heroes are taking center stage. Today’s innovations aren’t just about blocking out air and moisture; they’re about blending high-tech protection with bold sustainability, smart design, and even a touch of artistry.
Looking ahead, the real magic will come from brands and makers who see barrier layers as a canvas for creativity and responsibility. Imagine tubes that keep formulas potent, delight your senses, and tread lightly on the planet—all at once. The evolution of barrier technology isn’t just a technical upgrade; it’s a chance to reimagine what beauty packaging can be: protective, beautiful, and genuinely good for the world.