Sunscreen is often thought of as a summer essential, primarily associated with beach outings and vacations under the sun. However, its importance goes far beyond seasonal use. Every day, whether the sky is clear or overcast, our skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can penetrate clouds and cause cumulative damage over time. Prolonged exposure to UV rays is a leading cause of premature aging, sunburn, hyperpigmentation, and even serious health risks like skin cancer.
Despite the well-documented benefits of sunscreen, misconceptions about its necessity, effectiveness, and proper usage still prevent many people from incorporating it into their daily skincare routine. Some believe that darker skin tones are naturally protected, that sunscreen is unnecessary indoors, or that high SPF values provide complete immunity from sun damage. These myths contribute to inadequate sun protection, leaving the skin vulnerable to long-term harm.
This comprehensive guide delves into the science behind sunscreen, how it works to shield the skin from harmful radiation, and the key factors to consider when selecting the right formulation.

1. Why Sunscreen is a Skincare Essential
• Protection Against Harmful UV Rays
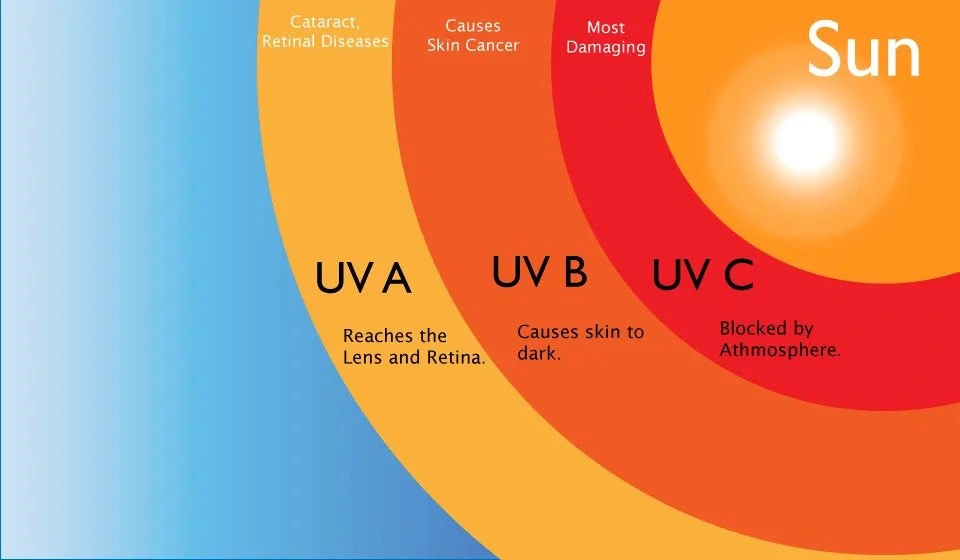
The sun emits ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is invisible to the naked eye but has profound effects on the skin. There are two primary types of UV rays that impact our skin:
UVA Rays: The Silent Skin Agers
- Penetrate deep into the skin, reaching the dermis (the skin’sthickest layer).
- Cause premature aging by breaking down collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and fine lines.
- Are present year-round, even on cloudy days, and can pass through glass windows, meaning indoor exposure is possible.
UVB Rays: The Cause of Sunburn and Skin Cancer
- Affect the outer layer of the skin, causing sunburn and DNA damage.
- Play a key role in skin cancer development, including melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
- UVB intensity varies by season and location but is strongest between 10 AM and 4 PM.
How Sunscreen Protects Your Skin
Sunscreen acts as a shield, absorbing or reflecting UV radiation before it can penetrate the skin. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays, preventing:
- Immediate damage like sunburn
- Long-term effects such as wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, and sagging
- DNA mutations that may lead to skin cancer
• Prevention of Premature Aging
Premature aging, also known as photoaging, is primarily caused by prolonged exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays. Unlike natural aging, which occurs over time due to genetics, photoaging is preventable with proper sun protection.
How UV Rays Accelerate Skin Aging
- Collagen and elastin breakdown: UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, degrading collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining firmness and elasticity. This results in fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging.
- Uneven skin texture and enlarged pores: Sun damage can weaken the skin’sstructure, leading to roughness and an uneven surface.
- Hyperpigmentation and sunspots: UV exposure stimulates excess melanin production, causing dark spots, discoloration, and an uneven complexion over time.
The Role of Sunscreen in Anti-Aging
Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily creates a protective barrier against UVA and UVB rays, preventing:
• Wrinkles and sagging by preserving collagen and elastin
• Dark spots and uneven skin tone caused by sun-induced pigmentation
• Loss of skin firmness and elasticity that contributes to premature aging
Scientific Backing
A landmark study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that daily sunscreen use reduces skin aging by 24% compared to those who apply it occasionally. This reinforces sunscreen as one of the most effective anti-aging products available.
By making sunscreen a daily habit, you can preserve your skin’s youthfulness, maintain a smooth complexion, and prevent premature signs of aging—proving that prevention is always better than correction.
• Reduced Risk of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer worldwide, and UV radiation is a major contributing factor. Excessive sun exposure damages skin cells at the DNA level, increasing the risk of developing melanoma, basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)—the three most common types of skin cancer.
How Sunscreen Helps Prevent Skin Cancer
- Blocks harmful UV rays: Broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB radiation, preventing cellular mutations that can lead to cancer.
- Prevents cumulative damage: Sun exposure adds up over time, and even short, daily exposure can contribute to long-term skin damage. Regular sunscreen use minimizes this risk.
- Reduces pre-cancerous lesions: Studies show that sunscreen can help prevent actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin condition caused by sun exposure.
Scientific Evidence
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, using sunscreen daily reduces the risk of squamous cell carcinoma by 40% and melanoma by 50%. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that consistent sunscreen use significantly lowers the incidence of invasive melanoma.
Sun Protection for All Skin Tones
A common myth is that people with darker skin tones are not at risk for skin cancer. While melanin provides some natural protection, it does not eliminate the risk. Skin cancer can be more dangerous in darker skin tones because it is often diagnosed at a later stage.
• Prevention of Hyperpigmentation and Dark Spots
Hyperpigmentation occurs when UV radiation triggers an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. This leads to dark spots, sunspots, and an uneven complexion. Individuals with melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and age spots are particularly vulnerable, as sun exposure can worsen discoloration and make it more challenging to treat.
How UV Rays Contribute to Hyperpigmentation
- Stimulates melanin production: UV exposure activates melanocytes, leading to dark patches and sun-induced spots.
- Worsens existing pigmentation: Conditions like melasma and PIH become more pronounced when exposed to sunlight.
- Delays skin healing: Sun damage can slow down the skin’snatural recovery process, making discoloration last longer.
The Role of Sunscreen in Preventing and Treating Hyperpigmentation
Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30+ daily can:
• Prevent new dark spots from forming by shielding the skin from harmful UV rays
• Reduce existing pigmentation by allowing the skin to heal without additional damage
• Even out skin tone by minimizing sun-induced discoloration
Best Sunscreen Practices for Hyperpigmentation
- Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Look for tinted sunscreens with iron oxides, which provide additional protection against visible light that can also contribute to pigmentation.
- Reapply every two hours, especially if spending extended time outdoors.
• Protection Even on Cloudy or Indoor Days
A common misconception is that sunscreen is only necessary on sunny days or during outdoor activities. However, UV rays are always present, even when the sun isn’t visible. Failing to apply sunscreen on cloudy or indoor days can result in cumulative skin damage over time.
How UV Rays Affect Your Skin Year-Round
- Up to 80% of UV rays penetrate through clouds, meaning your skin is still exposed on overcast days.
- UVA rays pass through glass, so you’re at risk even when indoors, driving, or sitting near a window.
- Snow, sand, and water reflect UV radiation, intensifying sun exposure even when it’snot sunny.
2. SPF Explained: How to Choose the Right Protection
• Understanding SPF Ratings
SPF (Sun Protection Factor) is a key indicator of how well a sunscreen protects against UVB rays, the type of radiation responsible for sunburn and contributing to skin cancer. While SPF ratings are often associated with higher protection, it’s important to understand how they actually work and the marginal differences in effectiveness between them.
How SPF Works
SPF measures the amount of UVB exposure required to cause sunburn on protected skin compared to unprotected skin. For example, if you would typically burn after 10 minutes of sun exposure, an SPF 30 sunscreen would allow you to stay in the sun for 30 times longer (i.e., 300 minutes) before burning. However, this doesn’t mean you can skip reapplying sunscreen after longer exposure.
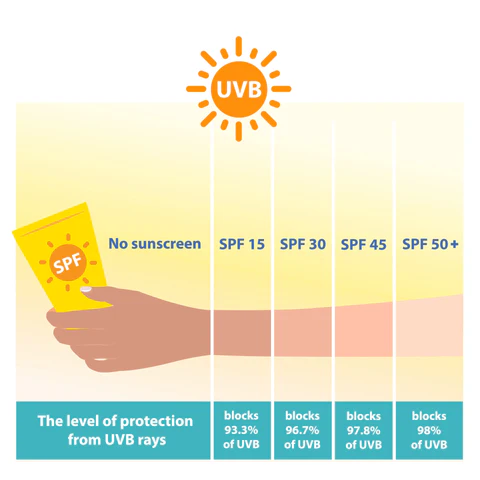
SPF Protection Breakdown
- SPF 15: Blocks about 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30: Blocks about 97% of UVB rays.
- SPF 50: Blocks about 98% of UVB rays.
- SPF 100: Blocks about 99% of UVB rays.
While higher SPF offers slightly better protection, the difference is marginal beyond SPF 30. For example, SPF 30 blocks just 4% more UVB rays than SPF 15.
• Broad-Spectrum Protection: Why It Matters
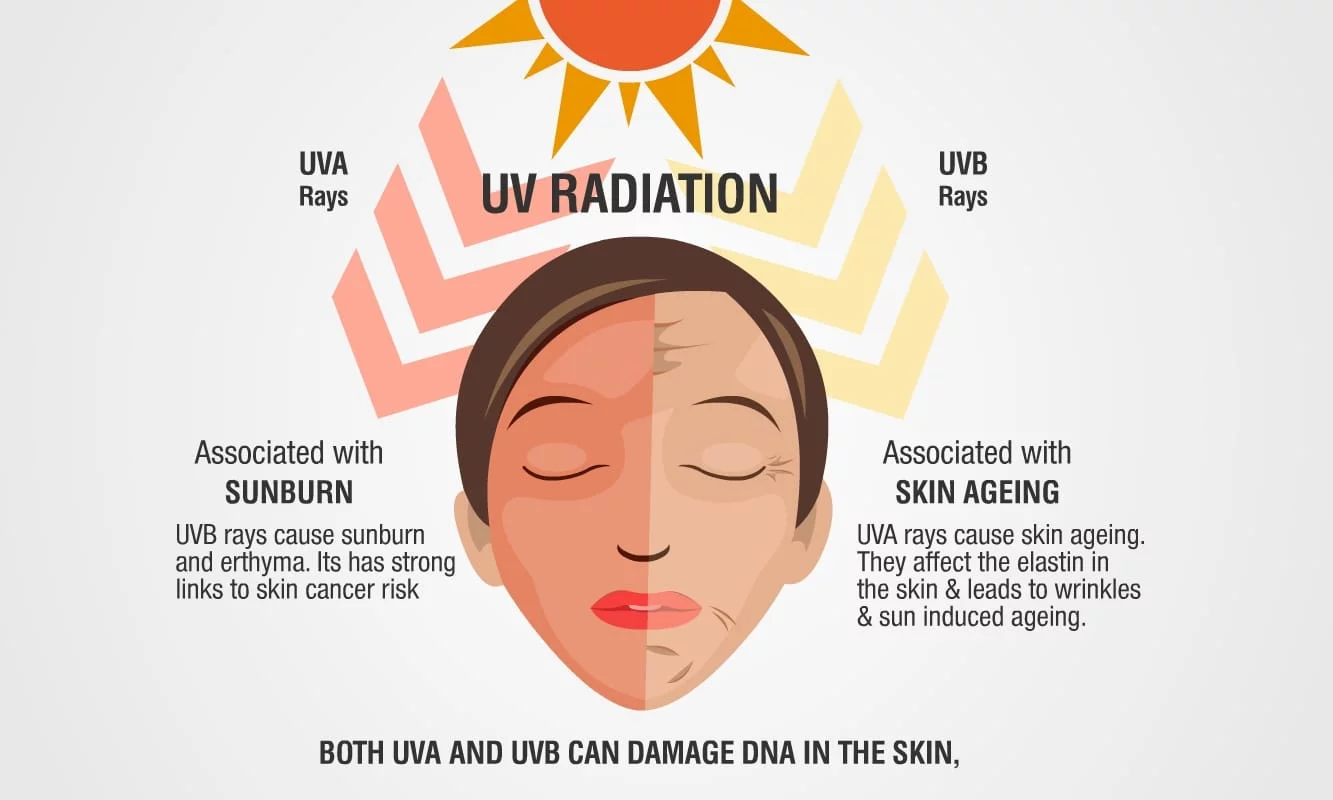
While SPF measures a sunscreen’s ability to protect against UVB rays, it doesn’t account for protection against UVA rays—which are equally important for skin health. UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and are the primary cause of photoaging (premature aging) and skin cancer. To ensure comprehensive protection, it’s essential to use sunscreen that offers broad-spectrum coverage.
The Difference Between UVA and UVB Rays
- UVB Rays: These are the primary cause of sunburn and contribute to skin cancer. However, they affect the outer layers of the skin.
- UVA Rays: UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and contribute to wrinkles, fine lines, sagging, and sunspots. They also play a significant role in the development of skin cancer, especially melanoma.
Why Broad-Spectrum Protection is Crucial
- Prevents Photoaging: UVA rays cause collagen and elastin breakdown, leading to the early formation of wrinkles and sagging. Broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against these aging effects.
- Reduces Skin Cancer Risk: Both UVA and UVB rays contribute to DNA damage, increasing the risk of skin cancer. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both types of radiation, significantly reducing this risk.
- Protects Year-Round: UVA rays are present year-round, even on cloudy days or indoors near windows. Broad-spectrum protection is essential, no matter the weather or environment.
• Choosing Between Chemical and Physical Sunscreens
When selecting a sunscreen, you’ll encounter two primary types: chemical and physical (mineral) sunscreens. Each type works differently to protect your skin from harmful UV rays, and understanding their differences can help you choose the right one for your skin type and preferences.
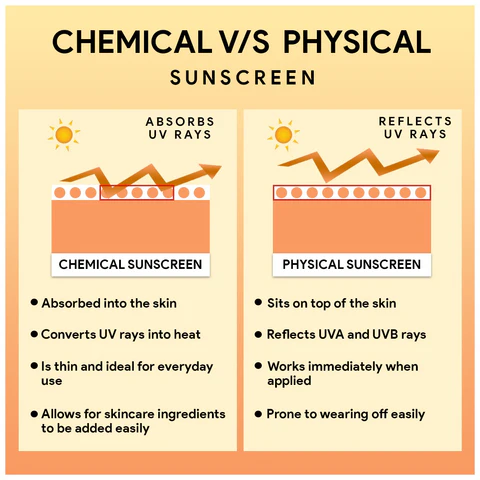
- Chemical Sunscreens
How They Work: Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays through active ingredients, then convert them into heat, which is released from the skin. This process prevents UV rays from damaging the skin’s deeper layers.
Pros:
Lightweight and often less visible on the skin.
Tend to blend in easily, leaving less of a white cast compared to physical sunscreens.
Cons:
Can sometimes cause irritation or allergic reactions, particularly in sensitive skin.
Not ideal for those with skin conditions like eczema or rosacea.
Needs to be absorbed into the skin to be effective, so reapplication after sweating or swimming is crucial.
- Physical (Mineral) Sunscreens
How They Work: Mineral sunscreens sit on the surface of the skin and create a physical barrier that reflects and scatters UV rays. The two main active ingredients are zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, both of which offer broad-spectrum protection.
Pros:
Provides instant protection as it works on the surface of the skin, without needing absorption.
Gentler on sensitive skin, making it a great option for those with conditions like rosacea, acne, or eczema.
Less likely to cause irritation or allergic reactions.
Cons:
May leave a white cast on the skin, especially for those with darker skin tones.
Can feel thicker or greasier than chemical sunscreens, which may not be preferred by those with oily or acne-prone skin.
- Choosing the Right Sunscreen for You
For Sensitive Skin: If you have sensitive skin or conditions like rosacea or acne, mineral sunscreens may be the better option due to their gentle formula and reduced risk of irritation.
For Daily Use or Active Lifestyles: Chemical sunscreens are often preferred because they tend to be lightweight, non-greasy, and more aesthetically pleasing, especially for those who are active or sweat a lot.
For Natural and Reef-Safe Options: Mineral sunscreens are typically reef-safe and less harmful to aquatic life, making them the preferred choice for those concerned about environmental impact.
• Water Resistance and Reapplication
Many sunscreen labels indicate a level of water resistance, typically for 40 minutes or 80 minutes, but it’s important to understand that no sunscreen is completely waterproof. Water-resistant sunscreens are designed to maintain their level of protection for a set amount of time when exposed to water, but they lose effectiveness over time and require reapplication after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
What Does Water Resistance Mean?
Water-resistant (40 minutes): Offers protection for up to 40 minutes in water. After that, you need to reapply.
Very water-resistant (80 minutes): Offers protection for up to 80 minutes in water before reapplication is needed.
While water-resistant sunscreens help maintain protection during physical activities, they are not immune to wear off. Activities such as towel drying, swimming, or heavy sweating will diminish the sunscreen’s effectiveness, meaning you should always reapply after these activities.
• Sunscreen for Different Skin Types
Selecting the right sunscreen for your skin type ensures optimal protection while addressing specific needs like oil control, hydration, and sensitivity. Here’s a breakdown of how to choose the best sunscreen based on your skin type:
- Normal Skin
Normal skin is well-balanced, neither too oily nor too dry. It has a smooth texture, small pores, and good blood circulation, giving it a healthy glow.
Recommended ingredients:
Hyaluronic Acid & Glycerin, Niacinamide, Aloe Vera & Green Tea Extracts moisturize and soothe the skin.
Antioxidants such as Vitamin C & Vitamin E provide additional protection.
Zinc Oxide & Titanium Dioxide (Physical/Mineral Sunscreens) provide gentle, broad-spectrum protection.
- Oily Skin
If you have oily or acne-prone skin, you’ll want a sunscreen that provides sun protection without clogging pores or making your skin feel greasy.
Recommended ingredients:
Niacinamide to help reduce shine and control oil production.
Silicone-based formulas for a smoother finish.
- Dry Skin
Dry skin can feel tight or rough, so it’s essential to choose a sunscreen that hydrates and nourishes the skin while providing protection.
Recommended ingredients:
Hyaluronic acid to retain moisture and keep skin plump.
Glycerin to help draw moisture to the skin.
Ceramides to restore and maintain the skin’s natural moisture barrier.
- Sensitive Skin
Sensitive skin can react to various ingredients in sunscreens, so choosing a gentle formula is key to avoiding irritation or allergic reactions.
Recommended ingredients:
Zinc oxide: Provides gentle, broad-spectrum protection and is suitable for sensitive skin.
Aloe vera and calming botanicals to reduce irritation.

3. The Role of Sunscreen Packaging in Sunscreen Preservation
While sunscreen formulation plays a crucial role in protecting the skin from harmful UV radiation, the packaging of sunscreen is equally important in preserving its effectiveness. Sunscreen’s active ingredients, whether chemical or mineral, can degrade when exposed to light, heat, air, and contamination, reducing their ability to shield the skin properly.
Protection Against Light and UV Exposure
Since many sunscreen formulations are sensitive to UV rays, exposure to sunlight can cause ingredient breakdown. Opaque bottles, UV-protective packaging, and airless pump dispensers help maintain the product’s stability by preventing light penetration and oxidation.
- Prevention of Oxidation and Contamination
Frequent exposure to air and bacteria can degrade sunscreen ingredients over time. Airless pumps, sealed tubes, and stick formats reduce contact with air and hands, maintaining the formula’s integrity and ensuring hygienic application.
- Heat Resistance and Shelf Life
Sunscreen is often used in outdoor environments, where it is exposed to high temperatures. Heat can cause separation of ingredients, reducing effectiveness. Thermal-resistant tubes, double-layered packaging, and insulated containers help minimize temperature-related degradation.
- Convenience and Reapplication
Reapplication is essential for maintaining sun protection, but inconvenient packaging can discourage proper use. Spray bottles, roll-ons, and compact travel-friendly designs improve ease of use, ensuring users can reapply sunscreen efficiently throughout the day.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact
With growing awareness of environmental issues, sustainable sunscreen packaging is becoming more popular. Recyclable materials, biodegradable packaging, and refillable bottles help reduce plastic waste while maintaining product effectiveness.
4. Conclusion
Sunscreen is more than just a skincare essential—it’s a daily shield against UV damage, premature aging, and skin cancer. However, its effectiveness depends not only on the formulation but also on the quality of its packaging. Without proper protection, light, air, heat, and contamination can degrade active ingredients, reducing their ability to safeguard the skin.
To ensure long-term stability and user convenience, sunscreen packaging must be designed to preserve efficacy and enhance application. UV-resistant bottles, airless pumps, temperature-resistant tubes, and travel-friendly formats play a crucial role in maintaining product integrity. Additionally, as sustainability becomes a key industry focus, brands are turning to recyclable, biodegradable, and refillable packaging solutions to reduce environmental impact without compromising quality.
At Othilapak, we specialize in premium cosmetic packaging solutions that combine innovation, functionality, and sustainability. Our expertise in customized sunscreen packaging ensures that your products remain protected, visually striking, and easy to use, helping your brand stand out in the competitive beauty market. Whether you need airtight dispensers, eco-friendly packaging, luxury finishes, or ergonomic designs, we provide tailored solutions that align with your brand’s identity and consumer expectations.
Partner with Othilapak to elevate your sunscreen packaging. With our commitment to quality, sustainability, and cutting-edge design, we help brands create packaging that not only preserves the integrity of their products but also enhances their market appeal. Let’s work together to craft smart, sustainable, and high-performance packaging that sets your brand apart.


